Pouring a drizzle of olive oil into a pan might seem ordinary, but the oil itself is far from it. Kun Covington, a Utah-based olive oil sommelier, has transformed her passion for olive oil into an immersive experience for anyone willing to taste and learn.
Covington regularly hosts olive oil tasting courses to share her expertise and help people select the right olive oil for their needs. Just like a wine sommelier who sniffs and tastes wine, an olive oil expert must learn the distinct flavors and identify any defects.
Here are some expert secrets to ensure you choose the best olive oil for your needs.

Secret 1: Determine your goal
Most consumers choose olive oil because it's considered healthier, but not all olive oils offer the same health benefits. Only real extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) delivers true health benefits. Therefore, it's important to know how to identify genuine EVOO. Just because a bottle is labeled "extra virgin" doesn't guarantee its authenticity.
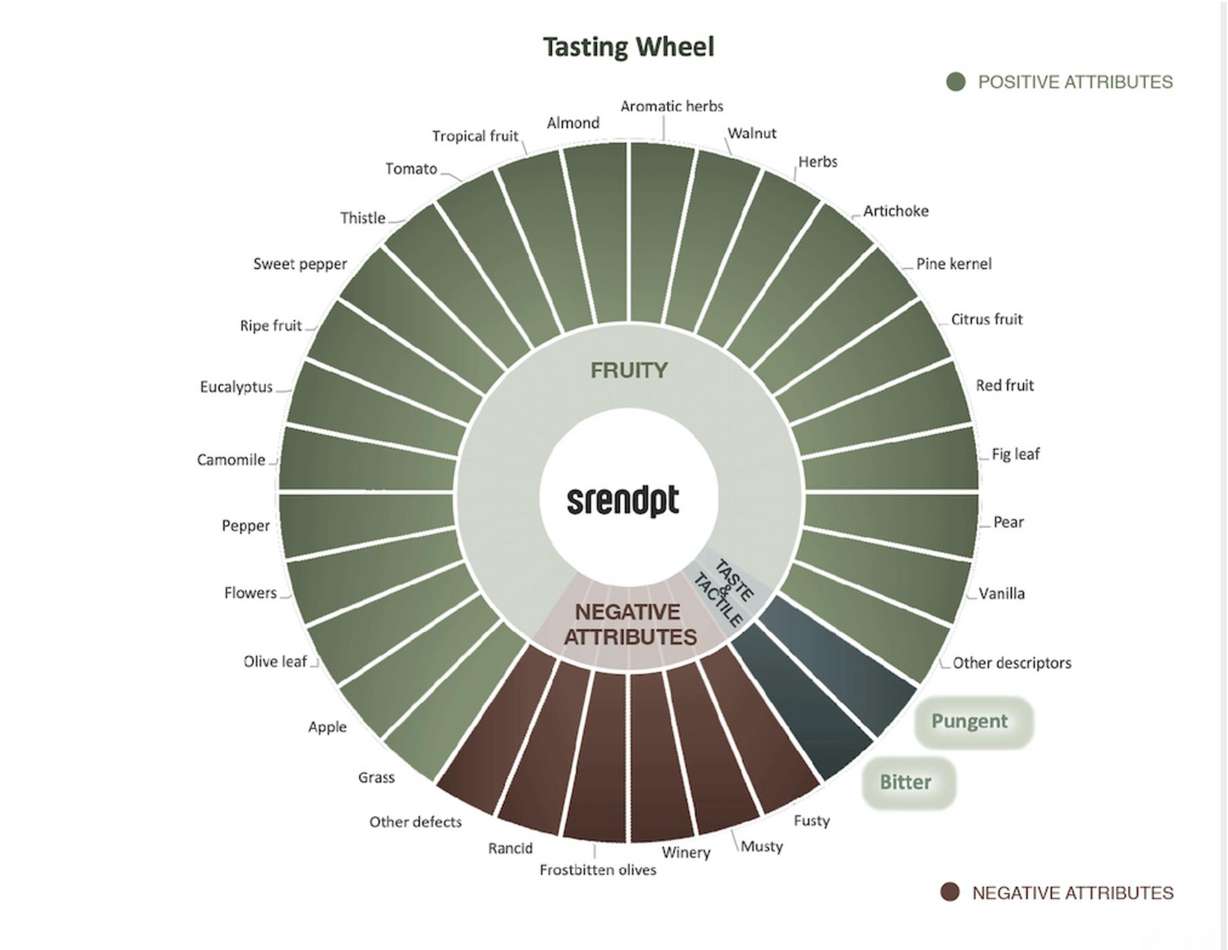
The only reliable way to confirm the quality of EVOO is to taste it. Real EVOO leaves your mouth feeling clean and refreshed after swallowing, unlike typical oils that feel sticky or greasy. Instead, it should invigorate you, much like drinking fresh juice.
High-quality EVOO should be fruity, bitter, and pungent.
For top-quality oil, consider Marsicani EVOO, available through Serendipity Trading. Their olive oils are imported from Italy and come from a well-respected third-generation family estate.
Secret 2: Recognize that 99% of the health benefits come from polyphenols
Polyphenols are nutrients found in plants that impart a bitter and peppery taste, helping to manage inflammation and possessing antioxidant properties. If you are concerned about heart health, aging skin, and autoimmune diseases, it is wise to choose an EVOO in polyphenols.
Secret 3: Extra Virgin Olive Oil is 100% Olive Juice!
Any olive oil containing additional ingredients cannot be classified as extra virgin. This means that rosemary or garlic-flavored olive oils do not qualify as true EVOO. Think of it like freshly squeezed orange juice — you wouldn't want to add anything that could detract from the juice's natural freshness and purity.
Although flavored oils may seem convenient for cooking, they often mask the flaws in the olive oil itself.
Secret 4: Find One That Complements Your Typical Meals
Olive oil is complex, much like wine. Certain EVOOs pair better with different foods. Here are some examples:
- Marsicani Alter Ego (Blue Label): Made from Itrana olives, with aromas of tomato leaves, grass, and green pepper. Best paired with white meats, vegetables, bread, and seafood.
- Marsicani Algoritmo (Red Label): Made from Frantoio olives, with notes of green olives, sweet almonds, artichoke, and chili pepper. Ideal for bread, pizza, pasta, and meats.
- Marsicani Viride Coratina (Green Label): Made from Coratina olives, with aromas of green olives, grass, arugula, and olive leaves. It has flavors of green almonds, artichoke, and a spicy pepper finish. Excellent with bread, vegetables, beans, and perfect for raw consumption, even with ice cream.
Secret 5: Air Freight in Original Bottles to Ensure Quality
Importing EVOO via air freight in its original bottles is essential for maintaining its quality. Air freight reduces the risks of temperature fluctuations and vibrations during transport, which can degrade the oil. While air shipping takes about a week, sea transport can take over a month, potentially compromising freshness.
Although it may increase costs, air freight preserves the oil's freshness and flavor. For example, Marsicani EVOO, imported by Serendipity, uses this method to guarantee superior quality. Keeping the oil in its original bottles also minimizes oxidation, further protecting its integrity.
If you choose imported EVOO, transporting it by air freight in its original bottles is the best way to guarantee premium quality.

Secret 6: Check the Harvest Date
Unlike wine, olive oil doesn't improve with age. When shopping for the perfect EVOO, check both the harvest date and the best-by date.
The best-by date is straightforward — use it by that date for the maximum flavor and freshness.
The harvest date is just as important. According to the North American Olive Oil Association, the harvest date refers to when the olives were picked from the trees.
The California Olive Oil Council recommends using EVOO within 18 months to 2 years of the harvest date. Purchasing from reputable vendors like Serendpity will ensure you get the highest-quality oil as close to the harvest date as possible.
Once opened, use it within three months.

Tasting: The Only True Measure of Quality
The only reliable way to assess the quality of EVOO is through tasting. Fresh EVOO is the best choice, as it's rich in polyphenols that provide powerful health benefits. However, if you know how to evaluate it, certain high-quality oils nearing their best-before date can still offer excellent quality.
Fresh EVOO should not be heated, as heat can degrade its polyphenol content –– It's best enjoyed raw. EVOO close to the best-before date, but still in good condition, is often more affordable and perfect for cooking, skincare, and other versatile uses.

Learn how to choose in person from an expert
Choosing olive oil can be complex, but learning how to identify the right oil from an expert can make all the difference. Covington offers olive oil tasting classes to help people identify the subtle yet important differences in different kinds of EVOO.
Some topics covered in her classes include:
- Why Choose Olive Oil?
- Types of Olive Oil
- The Olive Oil Production Process
- Standards for Quality Olive Oil
- Defects of Olive Oil
- Olive Oil Tasting
- Uses of Olive Oil
- Storage Tips for Olive Oil

Consider taking this continuing education class at the University of Utah's Lifelong Learning program, this class at Utah Valley University's Community Education, or private classes in Bluffdale.
To purchase award-winning, high-quality EVOO, browse the Marsicani collection at Srendpt.com.

















































